What Led to the Rise and Fall of the Mighty Ming Dynasty?
Explore the rise and fall of the mighty Ming Dynasty, known for its cultural and technological advancements, as well as its eventual downfall.

The Ming Dynasty, spanning from 1368 to 1644, was a time of remarkable cultural and technological advancements, but it also faced significant challenges that led to its eventual downfall.
The Rise of the Ming Dynasty

The Ming Dynasty was established in 1368 by Emperor Hongwu, who successfully overthrew the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty.
This marked the beginning of a new era characterized by strong central governance and a rekindled pride in Chinese culture.
A Vast and Diverse Dynasty
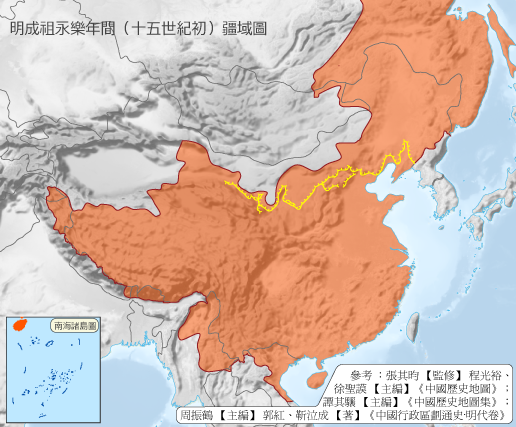
Covering over 6.5 million square kilometers at its peak, the Ming Dynasty was one of the largest empires in history.
Its territory expanded and reached its zenith under the reign of Emperor Yongle, fostering a diverse population of different ethnicities, languages, and religions.
This diversity led to a rich cultural exchange and artistic expression.
Cultural and Technological Advancements

The Ming Dynasty witnessed numerous cultural and technological advancements that contributed to its grandeur.
The arts flourished, with renowned artists producing exquisite paintings, porcelain, and calligraphy.
In addition, the dynasty made significant progress in fields such as agriculture, architecture, and shipbuilding.
The construction of the iconic Forbidden City in Beijing stands as a testament to the architectural prowess of the era.
Notable Figures
The Ming Dynasty boasted several notable figures who played pivotal roles in its history.
Emperor Yongle
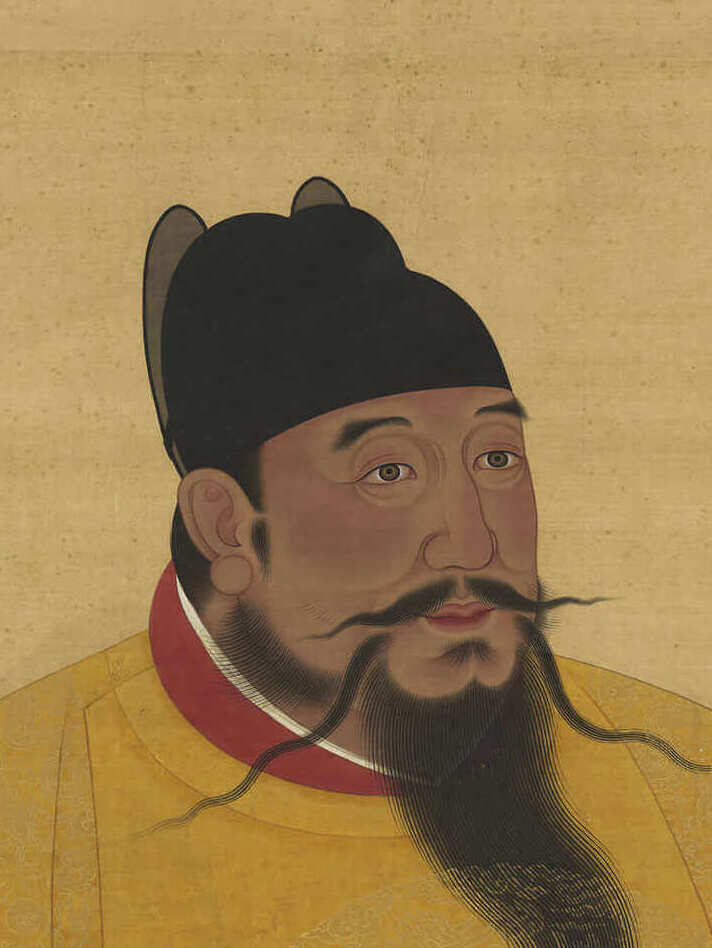

Emperor Yongle, in particular, spearheaded the expansion of the empire and sponsored the famed maritime expeditions led by Admiral Zheng He. These expeditions voyaged as far as Africa, showcasing China's naval power and establishing diplomatic links with other nations.
Tang Xianzu

Furthermore, literary figures like playwright Tang Xianzu and novelist Wu Cheng'en contributed immensely to the cultural wealth of the dynasty.
MO Ruzhong

MO Ruzhong was a military general and politician during the Ming Dynasty in China. He is best known for his role in defending the northern frontier against the nomadic Mongols.
Mo Ruzhong served as a commander in the Ming military and played a crucial role in protecting the Great Wall and repelling invasions from the northern tribes. His military achievements contributed to the stability of the Ming Dynasty's northern border during his time.
Achievements and Contributions

The Ming Dynasty made substantial contributions in various fields.
It implemented agricultural reforms, improving irrigation systems and introducing new crops, resulting in increased food production and economic prosperity.
The dynasty also established an impressive educational system, emphasizing literacy and Confucian principles.
Moreover, the invention of movable type printing by Bi Sheng revolutionized the dissemination of knowledge and played a crucial role in the preservation of classical Chinese texts.
The Downfall of Ming Dynasty

Despite its achievements, the Ming Dynasty faced numerous challenges that eventually led to its downfall.
Economic strain, external threats, and internal corruption weakened the once-mighty empire.
In 1644, the Ming Dynasty was overthrown by the Manchu forces, giving rise to the subsequent Qing Dynasty.






