How Does the Skin Absorb Toxins and Stay Hydrated?
Discover the science behind skin absorption and hydration, and how toxins penetrate the body.

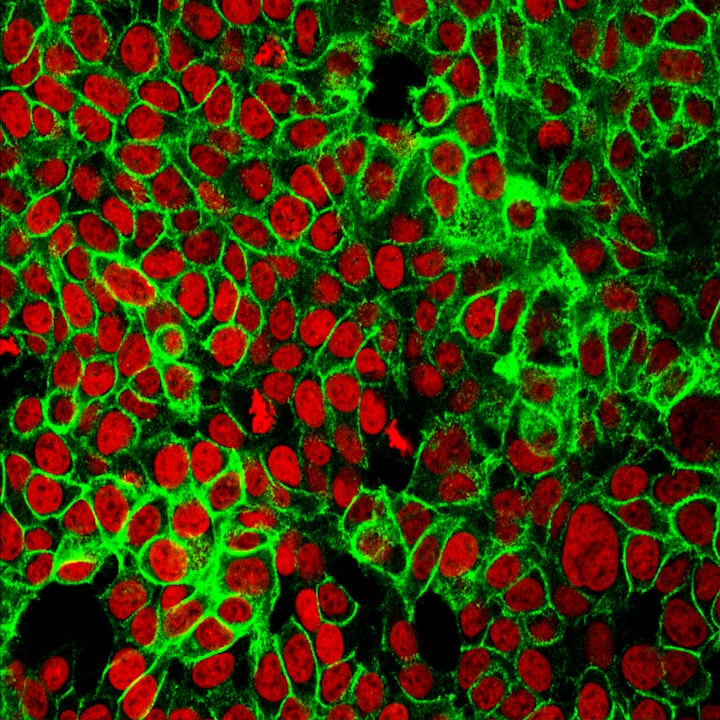
The human skin is a fascinating organ with the ability to absorb toxins and protect the body.
But, can it also effectively rehydrate the body?
Let's explore the science behind this complex question.
The Structure of the Skin
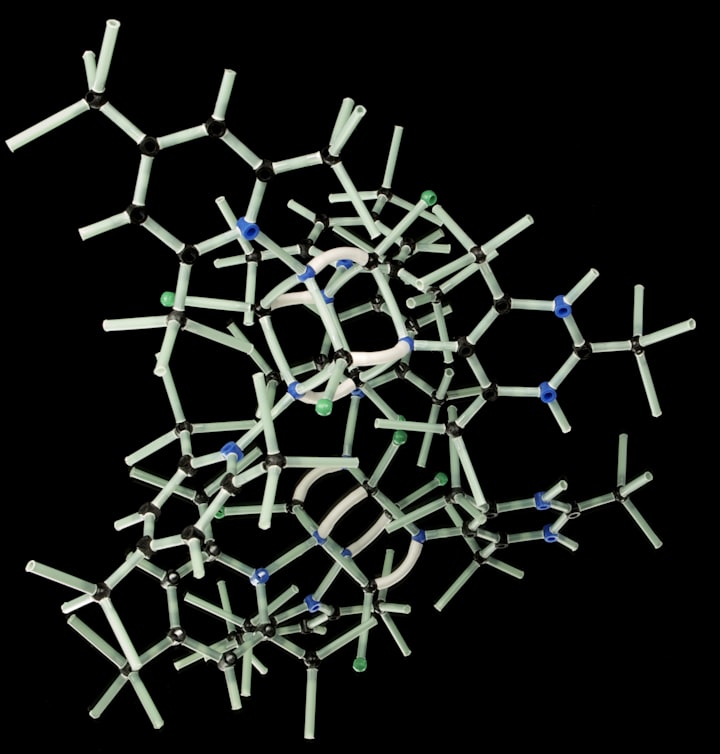
The skin is a complex organ with multiple layers, prominently featuring a protein called keratin.
When viewed under a microscope, the keratin forms chain-like structures, leaving minuscule gaps between them, allowing substances like water and toxins to pass through.
Skin's Absorption of Toxins
The keratin structure of the skin enables it to absorb various substances, including toxins.
However, this ability raises concerns about potential health risks associated with toxin absorption through the skin.
Skin's Hydration Process
Although the skin can absorb substances, it has limitations in rehydration.
While it prevents excessive water loss, it is not designed for significant water absorption.
The keratin, supported by the skin's natural oils, acts as a barrier against extensive water entry into the body.
Implications and the Future of Skin Science
Understanding the complexities of skin absorption and hydration has wide-ranging implications for healthcare and skincare practices.
This knowledge can lead to innovative developments in drug delivery systems, topical treatments, and hydration solutions.
The structure of the skin presents a constant interplay between absorption and protection, unlocking possibilities for medical and cosmetic advancements.